Single-Sided vs. Double-Sided vs. Multilayer PCBs: Which One Fits Your Needs?

When choosing a PCB, the number of copper layers matters. It affects not only cost but also design complexity, performance, and applications. Let’s quickly break down the three main types of PCBs.
Single-Sided PCBs
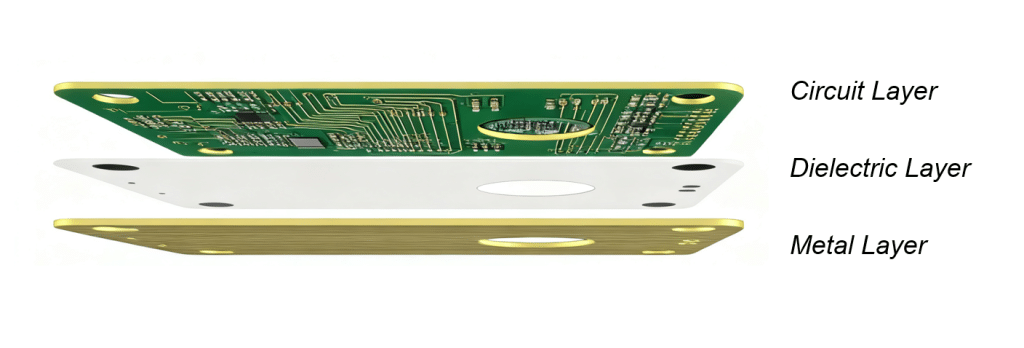
Layer Construction of Single-sided PCB
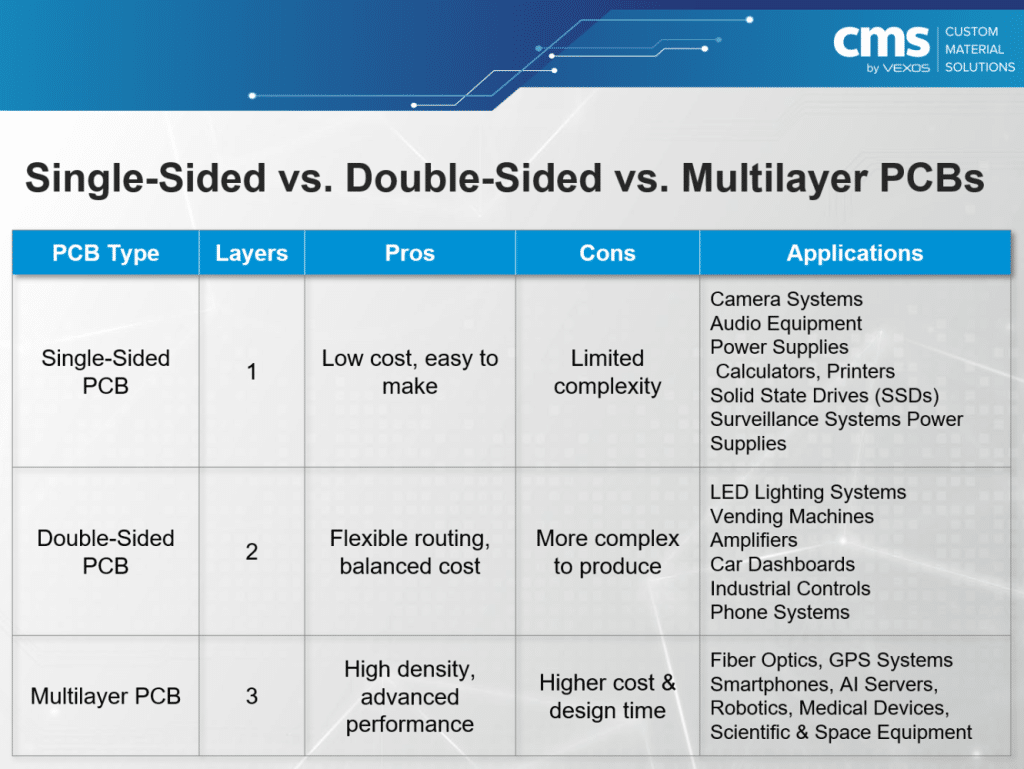
A single-sided PCB has copper traces on only one side of the board, while electronic components are mounted on the other. This is the simplest and most cost-effective PCB design, but routing is restricted to one surface, which limits component density and overall functionality. Single-sided PCBs are commonly used in devices where circuits are straightforward and cost is a major factor, such as calculators, basic lighting systems, and simple power supplies.
Double-Sided PCB

Layer Construction of Double-sided PCB
Double-sided PCBs feature copper layers on both sides of the board, with vias connecting circuits between the two layers. This structure allows for more flexible routing and higher component density compared with single-sided boards. While the manufacturing process is more complex and the cost is higher, double-sided PCBs offer significantly better performance. They are widely used in medium-complexity circuit designs, such as power modules, amplifiers, automotive electronics, vending machines, and industrial automation control systems.
Multilayer PCBs

Layer Construction of Multilayer PCB
Multilayer PCBs are made by stacking three or more copper layers separated by insulating layers, often with dedicated power and ground planes. This structure enables extremely high circuit density and excellent signal integrity, making them ideal for advanced applications. Multilayer boards are commonly found in smartphones, servers, medical instruments, aerospace electronics, GPS systems, and robotics. For example, modern AI server motherboards often include 20–30 power distribution layers combined with multiple HDI layers for high-speed signal interconnection, meeting the demands of ultra-fast computing. Although multilayer PCBs deliver outstanding performance, they also involve the highest design complexity, longest production cycle, and greatest cost.
Quick Comparison
Choosing the Right PCB Partner
Every PCB type has its role—from simple consumer devices to cutting-edge AI servers. At VEXOS CMS, we support custom PCB solutions ranging from 1 to 64 layers, offering a one-stop approach from prototyping to delivery.
All our products adhere to the industry-defining IPC standards for electronic assembly, ensuring maximum reliability for your chosen layer count.
👉 Learn more: https://cms.vexos.com/pcb
Important Note on Imagery: The illustrations in this article are AI-generated and are intended to serve as conceptual or supplementary material. Readers should be aware that specific technical accuracy or intricate professional details may vary from real-world components.
